Bridging Strategy and Execution in Healthcare Innovation
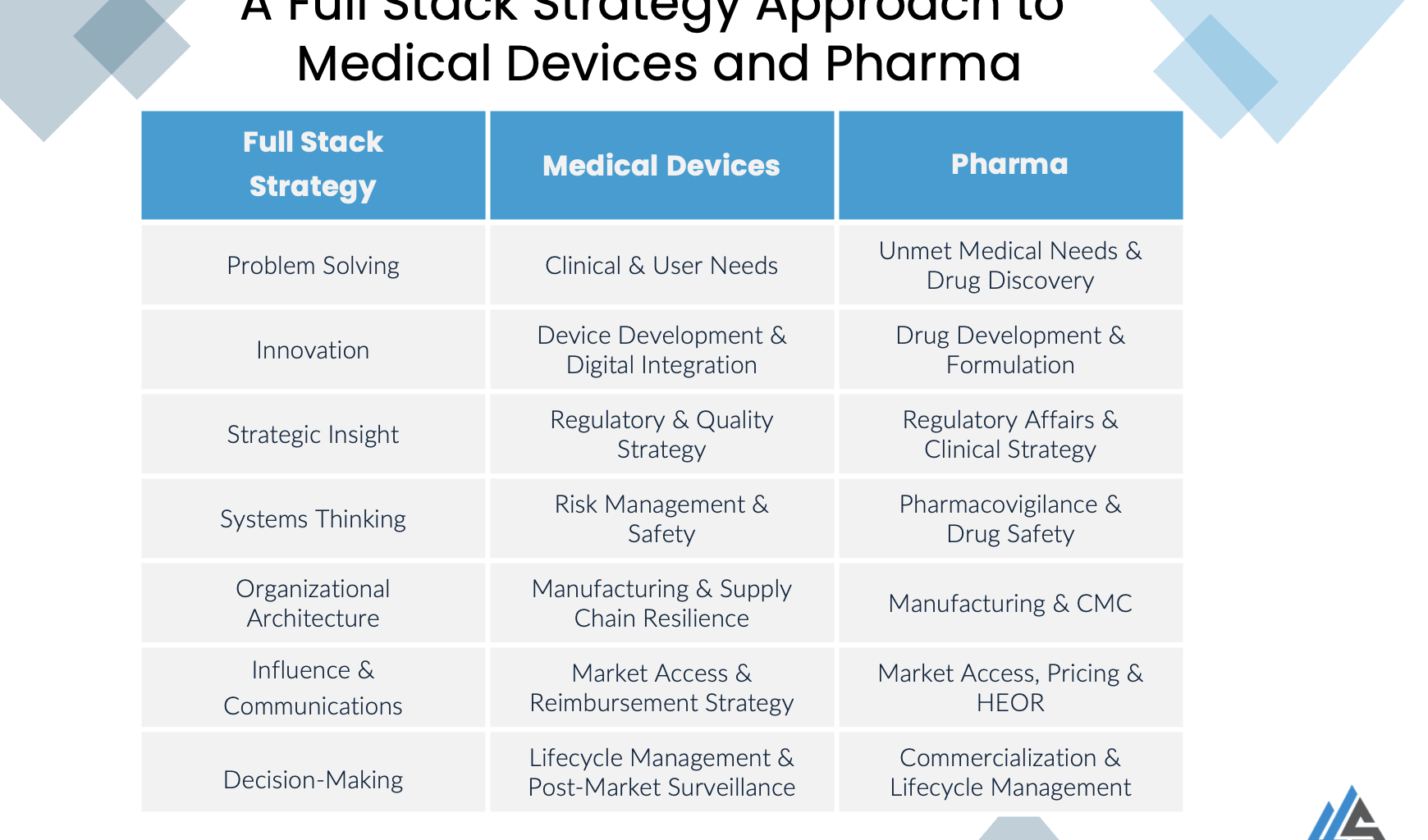
In the ever more complex playing field that we find ourselves in, medical devices and pharmaceutical organizations must navigate complex challenges from clinical unmet needs to regulatory compliance, from innovation to market access. A Full Stack Strategy approach ensures that every layer of the ecosystem, from problem identification to commercialization, is integrated for sustainable success. We aim to eliminate the regulatory gotchas and expensive redo of clinical trials.
This holistic perspective blends problem-solving, innovation, strategic insight, systems thinking, organizational architecture, influence, and execution to create transformative healthcare solutions. Let’s break down how this applies to both medical devices and pharmaceuticals.
We take the full stack approach and translate it to the domains of Medical Devices and Pharma. Full stack strategy practitioners have the knowledge and experience of working different siloed domains for example QA/RA, Production, Sales & Marketing and the expertise in breaking down these silos and bringing teams together to work in a truly cross functional manner.
1. Problem-Solving: Addressing Clinical and Market Needs
- Medical Devices: Understanding real-world clinical problems, user frustrations (healthcare providers, patients, and technicians), and unmet needs in healthcare settings is the foundation of impactful device innovation.
- Pharma: Identifying therapeutic gaps, rare diseases, and emerging healthcare burdens drives innovation in drug discovery and pipeline development.
Full Stack Practitioners must not only recognize these problems but also validate them through deep engagement with stakeholders, ensuring alignment with real-world needs.
2. Innovation: From R&D to Digital Integration
- Medical Devices: The convergence of AI, IoMT (Internet of Medical Things), and software-driven devices together with hardware and therapeutic combination devices is revolutionizing patient care. However, innovation must balance usability, clinical utility, and regulatory compliance as well as the key of therapeutic outcomes.
- Pharma: Advancements in biologics, gene therapy, mRNA, and small molecules require parallel innovation in drug delivery mechanisms, logistics, planning and new regulatory paradigms especially when patient derived therapies by nature yield evidence where n = 1 to maximize safety, efficacy, economics and patient adherence.
A Full Stack Strategist ensures that innovation is not just technologically groundbreaking but also practical, scalable, and aligned with clinical workflows.
3. Strategic Insight: Mastering Regulatory and Clinical Strategy
- Medical Devices: Companies must align their business strategy with ever evolving and fragmented regulatory frameworks such as ISO 13485, FDA (510(k), PMA), and MDR, ensuring that compliance is a strategic enabler rather than a hurdle.
- Pharma: Success in drug development requires expertise in FDA (IND, NDA, BLA), EMA, ICH, and GxP regulations, alongside optimizing clinical trial designs for faster approvals and cost efficiencies.
Understanding and integrating regulatory pathways early in development minimizes delays, de-risks investments, and ensures a smoother go-to-market process.
4. Systems Thinking: Risk Management & Safety as Core Principles
- Medical Devices: Embedding ISO 14971 risk management principles into device design, manufacturing, and post-market surveillance ensures patient safety and regulatory compliance. Rather than a paper exercise risk management needs to be embedded throughout the company.
- Pharma: Pharmacovigilance and drug safety demand continuous monitoring, risk-benefit analysis, and adherence to ICH E2E and E2C for global safety compliance just like medical devices risk should be a cultural habit not an administrative burden.
A systems-thinking mindset ensures risk mitigation is proactive rather than reactive, reducing costly recalls, liability and building trust in brands.
5. Organizational Architecture: Manufacturing and Supply Chain Resilience
- Medical Devices: Ensuring supplier compliance with ISO 9001, ISO 13485 and 21 CFR Part 820 while managing cost-effective manufacturing, design transfer, and scalability.
- Pharma: Managing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC), and CDMO partnerships to maintain quality and efficiency.
Supply chain resilience and operational agility are critical in an industry where regulatory demands and market shifts require rapid adaptation, particularly in a post COVID age where previous models of demand are still being over written.
6. Influence & Communication: Market Access and Reimbursement
- Medical Devices: Engaging payers, insurers, and hospital procurement teams to drive product adoption and reimbursement strategies.
- Pharma: Collaborating with PBMs (Pharmacy Benefit Managers), HTA (Health Technology Assessment) agencies, and payers to secure market access and pricing approval.
A Full Stack Strategist understands that clinical efficacy alone does not guarantee market success strategic engagement with stakeholders, payers, patient advocate groups, patients, clinicians and distributors is crucial for commercial viability.
7. Decision-Making & Implementation: Lifecycle Management & Post-Market Strategy
- Medical Devices: Post-market surveillance, complaint handling, recalls, and adherence to UDI (Unique Device Identification) and PMS (Post-Market Surveillance) requirements.
- Pharma: Managing drug launch strategies, patent expirations (Hatch-Waxman Act, biosimilar competition), and product differentiation for long-term commercial success.
Long-term success requires not only launching a product but also maintaining its market position seeing into the long term and managing IP life cycles through ongoing compliance, innovation, and strategic adaptation.
The Full Stack Strategist in Healthcare
A Full Stack Strategy approach ensures that every phase of the product lifecycle whether in medical devices or pharmaceuticals is interconnected. A Full Stack Practitioner has a vision on all the moving parts and layers of complexity and is able to zoom in and out at will. By integrating problem-solving, innovation, strategic insight, systems thinking, operational execution, and market influence, organizations can navigate complexity, reduce risk, and drive meaningful impact in healthcare.
For professionals looking to lead in this space, mastering this multi-layered approach is not just an advantage it’s a necessity. Whether you’re an executive, innovator, or policymaker, thinking full stack will position you at the forefront of healthcare transformation.